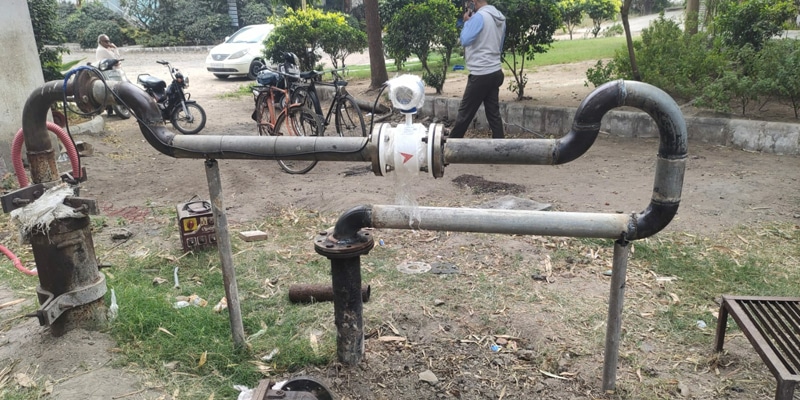
The world is becoming increasingly connected, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a pivotal role in this transformation. In industries like water management, agriculture, and even smart buildings, electromagnetic flow meters (EMFs) are taking center stage, empowered by IoT connectivity to deliver smarter, more efficient, and data-driven solutions.
But how exactly do these devices work, and how do they align with regulations like the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) guidelines in India? Let’s delve into the fascinating world of IoT-enabled EMFs and unlock their potential for you.
The Magic of Electromagnetic Flow Meters:
Imagine measuring the flow of water, oil, or even chemicals without physically interrupting the flow. That’s the magic of EMFs! They utilize Faraday’s law of induction, where a conductor moving through a magnetic field generates an electrical signal proportional to the flow rate. This non-intrusive approach makes them ideal for various applications.
The IoT Advantage: Connecting Meters to Insights:
Now, add the power of IoT to the mix. These EMFs can be equipped with wireless modules, transmitting data seamlessly to central hubs or cloud platforms. This real-time data flow opens doors to a treasure trove of insights:
Remote Monitoring: Track flow rates, consumption patterns, and potential leaks from anywhere, anytime.
Data-Driven Decisions: Analyze trends, identify inefficiencies, and optimize resource utilization for cost savings.
Predictive Maintenance: Detect anomalies and potential equipment failures before they disrupt operations.
Smart Automation: Integrate with control systems to automatically adjust processes based on real-time data.
Applications Abound: Where EMFs Shine:
From industrial giants to precision agriculture, EMFs are finding diverse applications:
Industrial Monitoring: Track water, oil, and gas consumption in factories, refineries, and power plants.
Smart Irrigation: Manage water usage in farms, ensuring optimal crop growth and minimizing waste.
Smart Buildings: Monitor water and energy consumption in buildings, leading to reduced utility costs and improved sustainability.
Environmental Monitoring: Track water quality, flow rates, and pollution levels in rivers, lakes, and aquifers.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: CGWA Guidelines in India:
When using EMFs for groundwater monitoring or extraction in India, adhering to the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) guidelines is crucial. These guidelines aim to ensure sustainable water management and prevent overexploitation.
It’s essential to stay updated on relevant regulations and obtain necessary permits before deploying EMFs for groundwater applications. Consulting with experts and water management authorities can help you navigate these regulations effectively.
Ready to Embrace the Future with IoT-Enabled EMFs?
The integration of EMFs with IoT technology presents a game-changing opportunity for industries that rely on efficient flow measurement and resource management. By understanding their working principles, diverse applications, and regulatory considerations, you can harness the power of these smart devices to achieve:
Increased Efficiency: Optimize resource utilization and reduce waste.
Enhanced Sustainability: Manage water and other resources responsibly.
Cost Savings: Minimize operational expenses and equipment downtime.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Gain valuable insights to inform strategic choices.